Stack Gas Emission Analyzers (CEMS)
CEMS (Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems) are designed for real-time and accurate monitoring of stack gas pollutants, with applications in power plants, petrochemical facilities, refineries, chemical plants, and more. These systems are typically installed to comply with environmental and legal regulations, though their data can also be used for combustion optimization.
Combustion of fuels such as natural gas, oil, and by-products of industrial processes typically generates the following pollutants:
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
- Unburned hydrocarbons
- Ammonia (NH₃) – usually residual from NOx reduction systems
Delta Gas Mobin Group’s Solutions
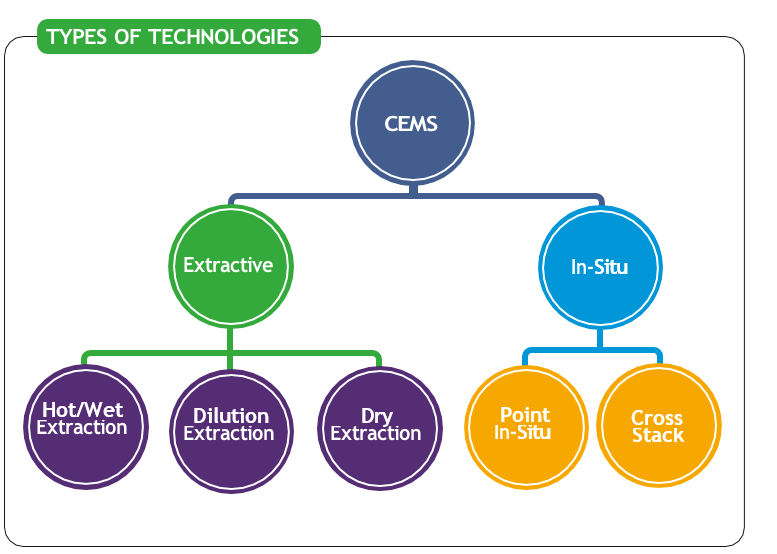
Delta Gas Mobin Group offers a full range of advanced technologies for stack gas measurement, tailored to suit diverse operational conditions. There are two primary approaches for stack gas analysis:
- In-Situ Measurement
In this method, sensors are installed directly in the flue gas stream. While simpler, this approach may lack the necessary accuracy or flexibility in complex industrial environments.
- Extractive Measurement
Here, a gas sample is extracted from the stack and transported to an analyzer unit. This approach is divided into three subcategories:
- Dilution Extraction Method
- Ideal for low-moisture applications such as coal combustion
- Involves mixing the gas sample with dry air to prevent condensation
- Limitation: Requires precise flow control; impurities can impact accuracy
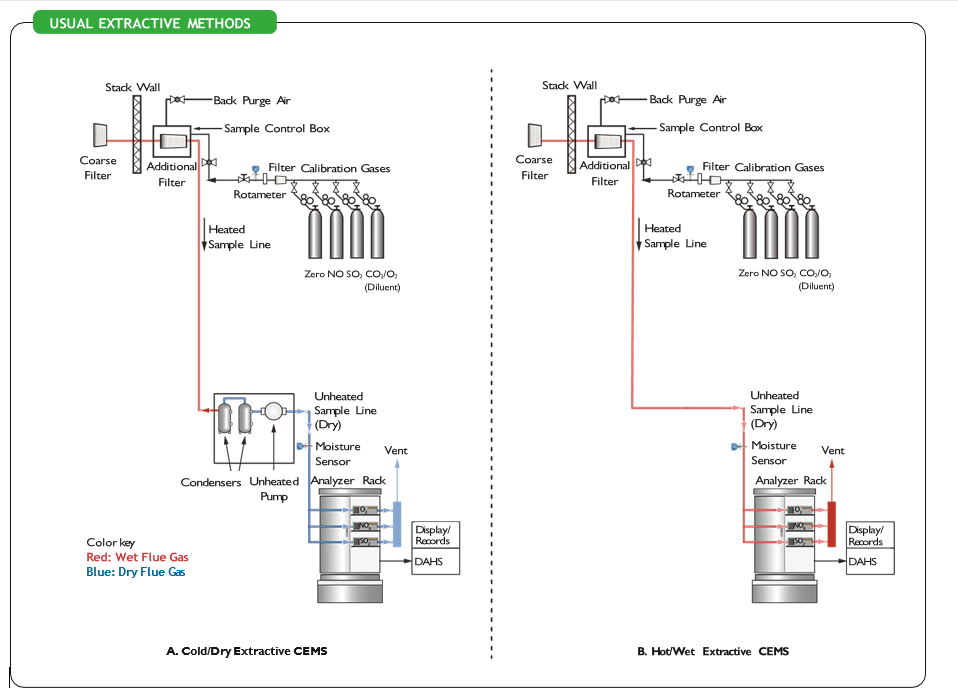
- Cold/Dry CEMS Method
- The most common method in petrochemical and chemical industries
- Gas is passed through a thermoelectric chiller (down to approx. 4°C) to remove moisture
- Limitation: Water-soluble analytes like NH₃, HCl, and HF may dissolve, reducing accuracy
- However, highly reliable for gases like NOx, CO, and SO₂ with minimal measurement errors
- Hot/Wet CEMS Method
- The gas sample is maintained at high temperatures (160–190°C) to prevent any condensation
- Suitable for gases with high SO₂ or HCl content
- All chemical components remain in gaseous form
- Mechanically simpler than Cold/Dry systems and suitable for precise measurement of sensitive analytes
Types of Gas Measurement Technologies
Depending on the type of gas and required accuracy level, different analyzers are used:
- Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR): For CO, CH₄, SO₂, NO, NH₃
- Non-Dispersive Ultraviolet (NDUV): For NO₂ and SO₂
- Gas Chromatography (GC): For measuring H₂S and other sulfur compounds
- Paramagnetic Analyzer: For O₂ measurement
- Chemiluminescent Analyzer (CLD): Reference method for NOx, compliant with EPA and EN 14792:2017 standards
The selection of technology depends on local regulations, fuel type, pollutant type, and expected measurement precision.
Advantages of Delta Gas Mobin Group’s Solutions:
- Fully aligned with international standards for emission monitoring
- Utilization of cutting-edge technologies
- Adaptable for installation in industrial and hazardous environments
- High accuracy and stability under harsh conditions
- Comprehensive after-sales services, training, and calibration